Building Your Dream Pallet Shed: A Step-by-Step Guide
Hey there, fellow DIY enthusiasts! So, you're dreaming of a backyard shed, but the thought of lumber prices and complicated building plans is making you want to curl up with a good book instead? Don't worry, I get it! That's why we're going to build a fantastic shed using reclaimed wooden pallets â€" cheap, cheerful, and surprisingly sturdy! This isn't your grandma's rickety pallet structure; we're talking a solid, usable space perfect for storing your garden tools, bikes, or whatever your heart desires. Let's get started!Phase 1: Planning and Preparation â€" The Foundation of Your Pallet Paradise
Before we even think about hammering a single nail, let's get organized. This phase is crucial for a smooth build and a shed you'll be proud of.Choosing Your Pallets
This is where the fun begins (and some serious scavenging might be involved!). You'll need a good number of pallets, depending on the size of your dream shed. Aim for sturdy pallets that are relatively clean and free of rot or extensive damage. Inspect them carefully â€" you want pallets that can handle the weight of your belongings. Don't be afraid to mix and match; slight variations in pallet appearance can add character to your shed.Shed Design & Dimensions
Now, let’s decide on the size and style of your pallet shed. Think about what you’ll be storing inside. A smaller 4ft x 6ft shed is perfect for tools and smaller equipment, while a larger 6ft x 8ft shed might suit bikes, outdoor furniture, or even a small workbench. Sketch out a basic design on paper. Remember, pallets are typically around 40 inches wide, so plan your dimensions accordingly. You might need to cut some pallets to make them fit your design. Don’t be afraid to get creative!Gather Your Tools and Materials
This is your essential toolbox checklist:- Hammer
- Screwdriver (preferably a drill/driver for speed)
- Measuring tape
- Level
- Circular saw (or hand saw, but be prepared for some serious work!)
- Safety glasses
- Work gloves
- Wood screws (various lengths)
- Pallet wood (obviously!)
- Optional: Plywood for sheeting or roofing, paint or sealant
Phase 2: Building the Foundation â€" A Solid Base for Your Shed
Now for the groundwork. A solid foundation is key to a long-lasting shed.Site Preparation
Find a level spot in your yard. Clear away any grass, weeds, or debris. You might need to level the ground using gravel or compacted soil. This ensures your shed sits evenly and won’t tilt over time.Constructing the Base Frame
This will likely require some sawing and assembly. You'll create a rectangular frame using sturdy pieces of pallet wood. The size should match the footprint of your planned shed. Securely fasten the frame together using screws. Consider adding concrete blocks or a simple wooden platform under the frame for added stability.Adding the Floor
You can create a floor from additional pallets, cutting them to fit within your frame. Alternatively, consider using plywood for a smoother, more waterproof floor. If using pallets, ensure they are securely fastened to the frame.Phase 3: The Walls â€" Raising the Walls of Your Pallet Haven
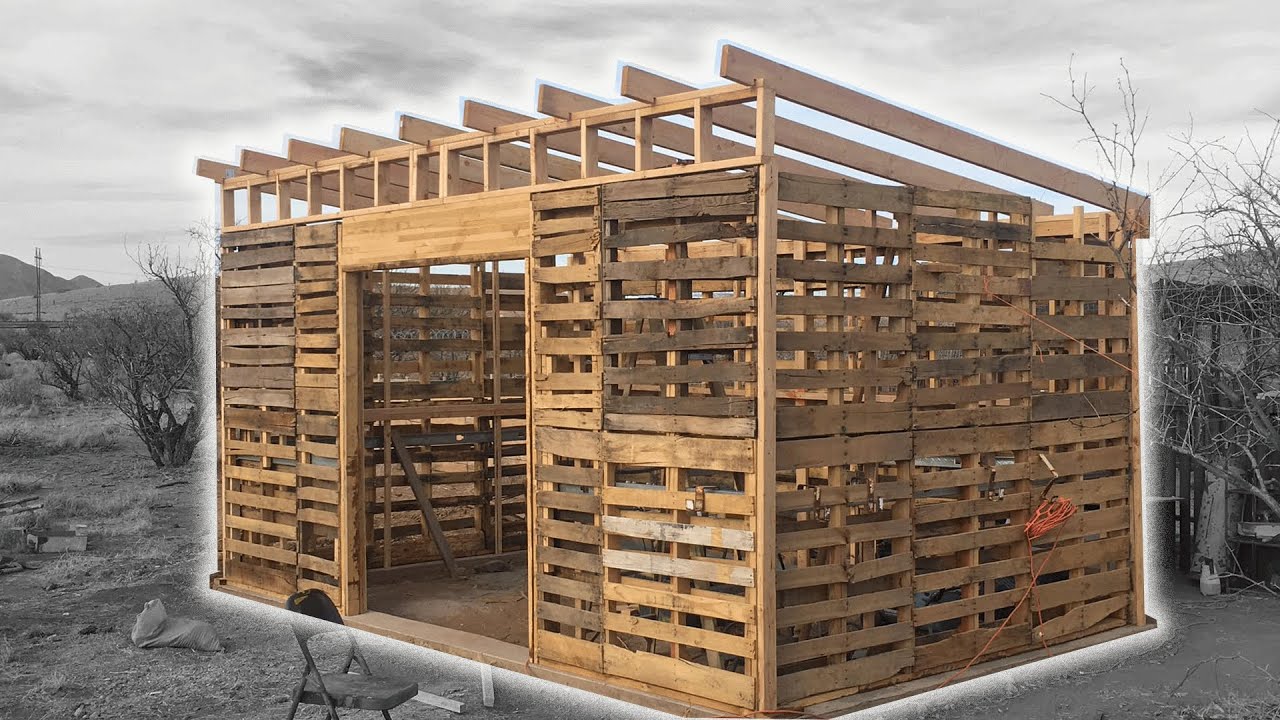
This is where the pallet magic really begins! You’ll be stacking pallets to create the walls of your shed.Wall Construction
Start by standing pallets upright against your base frame. Ensure they’re aligned and plumb (perfectly vertical). Secure them to the base frame using screws. You might need to cut some pallets to make them fit perfectly. Continue adding layers of pallets, ensuring each layer is securely fastened.Adding Support
For extra structural integrity, consider adding additional support beams or braces between the layers of pallets, particularly if your shed is tall or you plan to store heavy items. This will prevent the walls from bowing or collapsing.Doorway and Windows
Plan the location of your door and any windows you'd like to include. This might require cutting pallets precisely and carefully. Consider using plywood or reclaimed wood for framing the door and windows.Phase 4: Roofing â€" Sheltering Your Precious Possessions
A good roof protects everything inside.Roof Framing
Create a simple roof frame using sturdy pieces of pallet wood or other lumber. The exact design depends on your preference (gable roof, shed roof, etc.). Securely fasten the frame to the top of the walls.Roof Covering
Now for the final step! You can use plywood, corrugated metal sheeting, or even more pallets (though this might require more work). Secure your chosen roofing material to the frame, ensuring it's waterproof and weatherproof.Phase 5: Finishing Touches â€" Adding the Finishing Touches
Almost there! Let's make your shed look its best.Door Installation
Install your door using hinges and a latch. Make sure it opens and closes smoothly.Sealing and Painting
Apply a wood sealant to protect your shed from the elements. Consider painting it a color that complements your garden or landscape.Interior Finishing
Add any interior shelving or hooks you might need. This will help you keep your belongings organized.Commonly Asked Questions
Q: How long does it take to build a pallet shed?
A: The time it takes depends on the size and complexity of your design, and your experience level. You could build a small shed in a weekend, but a larger, more elaborate project could take several weekends.
Q: Are pallet sheds sturdy enough?
A: With proper construction, yes! The key is using strong, sound pallets and reinforcing the structure adequately with supports and screws. Don't overload your shed.
Q: What if I don’t have any pallet wood?
A: You can often find free or inexpensive pallets from local businesses (ask around!). Alternatively, you can purchase new lumber, though this will increase the cost.
Q: Do I need planning permission?
A: Building regulations vary by location. Check with your local council to determine if you need planning permission before starting your project. Size and location are crucial factors.
Q: How do I make my pallet shed weatherproof?
A: Using a waterproof roof covering is essential. Sealing the pallets with a good wood sealant will help protect them from moisture. A well-sealed roof and proper ventilation are also important.
There you have it! Your very own backyard pallet shed. Remember to prioritize safety and take your time. Don't hesitate to adapt this guide to suit your own creativity and resources. Happy building!